Oral Cavity
Formation of the secondary palate
Formation of secondary palate starts between week 7 and 8, and ends at around the third month of gestation.
Oral Cavity mainly consists of three outgrowths:
- The nasal septum grows downward from Frontonasal process along the midline
- The two palatine shelves, one at each side and extends from the maxilla towards the midline
Week 7:
- The two palatine shelves which arise from the bilateral maxillary processes, grow downward in a vertical direction on both sides of the tongue
- The tongue is withdrawn from between the shelves, and moves forward
- The intermaxillary segment and the maxillary prominence fuse together forming the upper lip
Week 8:
- The tongue and mandible are small relative to the upper facial complex.
- The lower lip is positioned behind the upper one
- The tongue occupies an elevated position between the palatine shelves
- The tongue has been depressed and the palatine shelves are elevated but not fused yet
- The palatine shelves slide over the tongue in a process called the palatine shelves elevation
- The facial complex (head) is folded into the developing thorax region
Week 9:
- The lower lip is positioned in advance to the upper lip
- The tongue is situated below the palatine shelves
- The tongue and lower jaw can grow forward, because the facial complex has lifted away from the thorax
- The palatine shelves continue to grow medially until they meet; this process is known as the palatine shelf closure
- A second fusion occurs between these two fused shelves and the primary palate at the midline of the nasal septum
- This fusion will lead to the separation of the primitive oral cavity into the oral cavity and nasal cavity
- Closure of the secondary palate proceeds from the primary palate
The Tongue
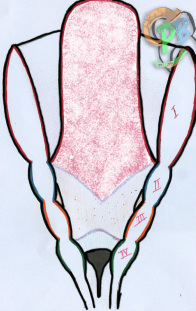
- Tongue formation starts at week 4 until week 12
- It is formed from the first, second, third and fourth pharyngeal arches, and from the occipital bone
- The anterior two thirds of the tongue are called the body, while the posterior third is called the base
- The body of the tongue is the movable part and it is made of:
1) Muscles
2) Connective Tissue
3) Epithelium tissue
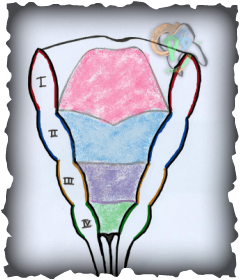
Stages of tongue development:
a. Copula (2nd arch)
b. Large hypobranchial eminence (3rd + 4th arches)
- A swelling (tuberculum impar) arises in the midline of the Mandibular process, and in between two lingual swellings.
- Then these three swellings (tuberculum impar + two lingual swellings) fuse together forming the anterior two thirds of the tongue.
- The large midline swelling which forms the root of the tongue is formed from the 2nd, 3rd, and 4th pharyngeal arches.
- The large midline swelling consists of:
a. Copula (2nd arch)
b. Large hypobranchial eminence (3rd + 4th arches)
- The hypobranchial eminence overgrows the copula causing it to disappear
- The posterior of the 4th arch develop the epiglottis
- Tongue is separated from the floor of the mouth after the formation of the lingual sulcus